
Book a demo
Health, disease and aging affect everyone. Everyone invests in their well-being, for prevention and treatment. Investments are based on data, which are collected at home, in hospitals, clinical research laboratories and mobile devices. For security and privacy reasons, the data is kept separately.
Federated learning offers the possibility to address these issues, both for the general population with features common to all and for the individual in the rare or unusual case.
The variability of applications and configurations is another strong point of Federated Learning offered by Sensoworks and Frontiere:
Hospitals could use federated learning models to predict the likelihood of an individual patient developing a disease or contracting an infection after being admitted. This could help doctors make better decisions about how best to treat each patient based on their specific needs. Additionally, these predictions could be used by other organizations that work with hospital patients (such as insurance companies) in order to provide better coverage options for those who need it most.
Another area where federated learning can benefit healthcare is by helping us understand diseases like cancer or Alzheimer's disease at the genetic level better. Using federated learning models on DNA samples collected from thousands of people suffering from these conditions, researchers can gain insight into which factors contribute most to the development of these diseases.
Federated learning provides interoperability gains that positively impact healthcare professionals quickly accessing a patient’s medical information even if they are not within the organization’s internal systems (e.g., patients visiting from another country), and applying analytics. High quality medical decisions could be ensured regardless of the patient's treatment location and local knowledge of the disease. Physicians can augment their expertise with expert knowledge from other institutions, ensuring consistency of diagnoses that would not be possible otherwise, improving the effectiveness of patient care and enabling greater collaboration in the healthcare sector.
Federated learning has been used in medical research because it allows researchers to create large sets of patient data that they can then use as part of their research efforts without needing direct access to any individual's private health information. It also allows researchers who may not have access to certain medical records or resources (such as patients' genetic information) to instead access those same resources through other researchers' databases. This prevents privacy breaches while still allowing researchers access to sufficient information and insights.
As healthcare and clinical-data is scattered, gathering a data set that is complete enough to track rare cases involves combining data from various data silos. The practical challenges of any single site lacking adequate and sufficient data for rare adverse drug reaction detection and prediction, can be addressed. Likewise federated learning can assist in reaching the cohort sizes for orphan/rare disease studies and ensuring ethnic genomic diversity.
Precision medicine is a growing field in healthcare. A precision medicine study is an experimental study that uses personal data to develop a personalized treatment plan for an individual patient. The aim of these studies is to direct the treatment based on an individual person's unique genetic profile and medical history. Federated learning can be used to predict things like disease progression or patient outcomes, but it can also be used to predict patient responses to medications or other treatments. Using federated learning to analyze large amounts of patient data could help researchers identify new approaches to treating diseases like cancer and Alzheimer's at the molecular level, which could lead to more personalized treatments for patients. With access to large data sets, more precise drugs can be developed in an accelerated way.
Home health monitoring has attracted great attention for aging populations around the world. With abundant user health data being accessed by Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart healthcare has seen many success stories. A personalized wearable device is used to collect, store and send health-related metrics, and can make medical recommendations for unusual health conditions. Nursing homes can offer specialized and constant care to the elderly. In these centers, remote health monitoring and recommendations can offer better services at reduced costs.
By unifying large data sets, new levels of well-being are offered at affordable costs.
Contact: dr. Remco Foppen
Fill out the form at the end of the page to request information on products or partnerships.
Waste management is a significant challenge for many cities worldwide. The amount of waste produced is constantly increasing, then an organised and efficient collection must be necessarily implemented. It must be efficient in order to provide timely and efficient service to citizens, and must aim to be more sustainable in terms of both environmental impact and the costs of management itself.
One of the biggest issue in waste management is the lack of information related to the waste flow. Often, waste managers do not have a complete understanding of the amounts and types of waste produced in a delimited area, making it difficult to efficiently plan the waste collection and disposal.
Moreover, many waste management systems are still manual and require a lot of time and human intervention to be performed correctly. This leads to higher costs and low efficiency in waste management.
All of this is primarily due to the presence of outdated infrastructure. Many waste management facilities are old and were not designed to support IoT technology. This makes it difficult to implement a smart picking system into existing infrastructure.
IoT (Internet of Things) technology is transforming many industries, and waste management is not an exception. IoT technology allows real-time data collection on the waste produced in a given area, and this data can be used to improve the management of the process. Here's how smart picking can improve waste management:
IoT can thus improve waste management by providing precise and real-time information on the waste produced in a given area, allowing for more efficient waste collection and disposal planning, reducing operational costs, and increasing the recycling rate.
Here are 4 brief examples showing the effectiveness of an IoT solution:
Fill out the form at the end of the page to request information on products or partnerships.
Smart manufacturing, or the connected factory, is a central concept in Industry 4.0 and represents an evolution of the traditional approach to production. Through the use of advanced technologies, sensors, and IoT devices, companies can achieve greater efficiency and flexibility in production, allowing them to adapt to market demands more quickly and efficiently.
The intelligent factory represents the endpoint of companies' digital transformation. The goal is to create a highly interconnected and flexible work environment, where machines, production systems, and IoT devices work together to optimise production and reduce costs.
The connected factory is based on three pillars: connectivity, digitalization, and automation.
Smart manufacturing is based on the interconnection of production systems and IoT devices. These devices can include sensors, actuators, motors, machinery, robots, mobile devices, and other elements that can collect information about production activities. This data is then sent to a cloud platform, where it can be analyzed and used to make informed decisions.
The interconnection of IoT devices also enables real-time monitoring and control of production activities. For example, an AI-based IoT platform can analyze data from sensors in real-time and identify any anomalies in production. The system can then adjust production accordingly, reducing machine downtime and improving product quality.
The use of advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and deep learning can lead to significant improvements in productivity and product quality. For example, an AI-based IoT platform can analyze large amounts of data in real-time, identify issues, and suggest solutions to improve production. Additionally, machine learning can be used to predict machine failures, reduce machine downtime, and prevent production interruptions.
Automation is another important feature of Smart manufacturing. Automation can be used to automate production activities and reduce personnel involvement in repetitive, low-value tasks. This can free up personnel to perform higher value-added activities such as design, innovation, and system maintenance.
The adoption of these technologies can lead to increased competitiveness for the company in the market, through reduced costs, increased productivity, and greater flexibility.
Many companies have already adopted Smart manufacturing and are achieving remarkable results.
For example, the German company Siemens has implemented a flexible production system that allows for quick and customized production of products requested by customers.
The American company General Electric has adopted a remote monitoring system based on IoT, which allows for real-time monitoring of machine performance and prevention of potential breakdowns.
According to a study conducted by McKinsey, the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and automation can lead to a 20-30% increase in productivity and a 10-20% reduction in costs.
Fill out the form at the end of the page to request information on products or partnerships.
A Smart Building is a structure that uses advanced technology to optimize its performance and improve the comfort, safety, and productivity of its occupants. They use a variety of sensors, devices, and systems to collect data from the building's facilities and environment and use this data to control and automate building functions such as heating, cooling, lighting and security.
One of the key components of a smart building is the use of an Internet of Things (IoT) platform, which serves as a central hub for data collection (monitor), analysis of building system data (predict) and for controlling and automating building functions (control).
IoT platforms often use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to analyze data and identify patterns and trends, which can be used to optimize building performance and make data-driven decisions.
Smart buildings can offer a wide range of benefits, such as increased energy efficiency, improved comfort and productivity for occupants, enhanced security and reduced maintenance costs. They also have the potential to play an important role in addressing global sustainability and environmental challenges.
After defining what a Smart Building is, we list the important aspects to consider based on our experience applied to the projects we have developed.

An intelligent IoT platform can address the issues of a Smart Building by providing advanced automation and analytics capabilities, therefore:
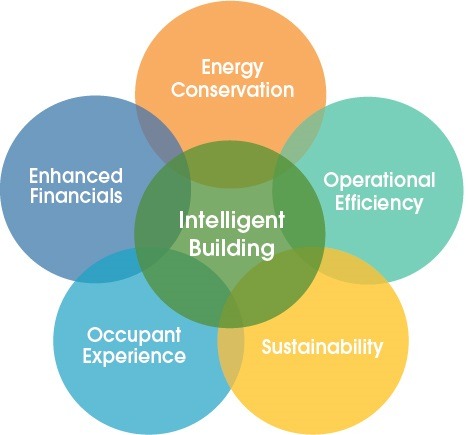
An intelligent IoT platform can provide several benefits in terms of cost reduction, sustainability, and social impact:
The exact percentage of cost reduction, energy savings, and other benefits depends on many factors such as the specific implementation and goals.
There are several studies from authoritative sources that have estimated the benefits under certain conditions.
For example, according to a study by the Rocky Mountain Institute, smart building projects can save building owners up to 20-30% on energy costs and up to 15-20% on maintenance costs.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) reported in a study that, on average, commercial buildings can achieve energy savings of up to 20% by implementing IoT-enabled building automation systems.
A study by the McKinsey Global Institute reported that IoT-enabled building systems can reduce energy consumption by 10-20% and improve overall building efficiency by 5-15%.
Fill out the form at the end of the page to request information on products or partnerships.
Public lighting is a relevant - and sometimes taken for granted - component of urban life, fundamental in terms of safety and comfort, but it is also used as an aesthetic element to adorn our cities by highlighting, for example, the historical monuments. However, up until now, its management and maintenance were often complex and expensive due to manual management that did not permit complete control on parameters such as consumption, faults, and various issues.
Now, thanks to IoT technology, public lighting is undergoing a revolutionary evolution that is changing the way we see and interact with our urban environment. With IoT, cities can become safer, more efficient, and more attractive, creating a “brighter” future for all of us.
The disconnected lighting can lead to various problems in the management of city public lighting:
IoT offers a solution to the problems listed above, thanks to its ability to gather together all the data coming from the various components of public lighting systems in real-time, allowing a more centralised and efficient management and a greater optimization of costs. For example, local authorities can monitor and control in real time public lighting systems remotely, identify any problems and intervene quickly to resolve them. Furthermore, IoT allows for better energy management, through automatic regulation of the light intensity according to needs
Therefore, the advantages in summary are:
Energy savings and cost reduction, of course, varies depending on several factors such as the size of the city or the amount of monuments to be illuminated. But some studies have shown that the adoption of connected public lighting systems can lead to an average energy savings of 40-60% and a cost reduction of up to 50% or even more in particular conditions.
In conclusion, connected public lighting represents an important step forward in managing the city and the lives of its residents. With its ability to improve safety, energy efficiency, and the comfort of public spaces, the adoption of connected lighting systems with IoT software solutions can bring a series of benefits to cities and their residents. Additionally, the adoption of connected lighting systems can help reduce environmental impact, improve the quality of life for citizens, and promote sustainable development of cities.
Fill out the form at the end of the page to request information on products or partnerships.
Cultural heritage is a fundamental component of a country's history and identity. Historical buildings, in particular, are tangible symbols of our heritage and have to be preserved for the upcoming generations. However, the preservation of these buildings is often complicated due to several practical facts and how to implement the proper systems of prevention without compromising the architectural aspects.
Luckily, technology is offering new solutions to preserve these precious treasures. Structural monitoring and predictive maintenance are two technologies that are making a significant difference in the preservation of historical buildings.
Monitoring involves the use of sensors and surveillance technologies to constantly monitor the structural integrity of buildings. Thanks to an IoT platform it is possible to collect and process a huge amount of data, which are collected from sensors installed in the structure. Monitor, detect, control the signs of degradation such as cracks or settling, and provide the maintenance team with useful information. This allows anomalies to be quickly identified and measures taken to prevent further deterioration.
On the other hand, AI algorithms are implemented for predictive maintenance, as a matter of fact algorithms analyse and train data collected from sensors and the outcome is a prediction about the maintenance plan that should be followed. This allows conservation managers to plan preventive maintenance instead of having to react only when problems become severe.
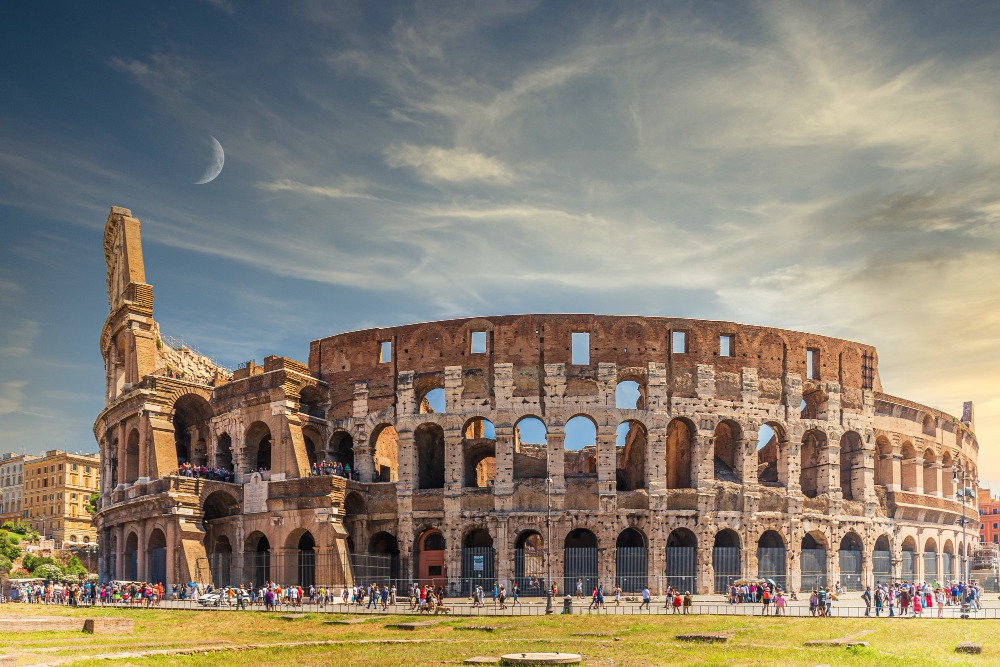

In Italy, these IoT technologies are already making a big difference in the preservation of historic buildings. For example, the Colosseum in Rome has been equipped with an advanced monitoring system that constantly monitors its structural integrity. This has allowed the identification of the anomaly and prevention from worsening.
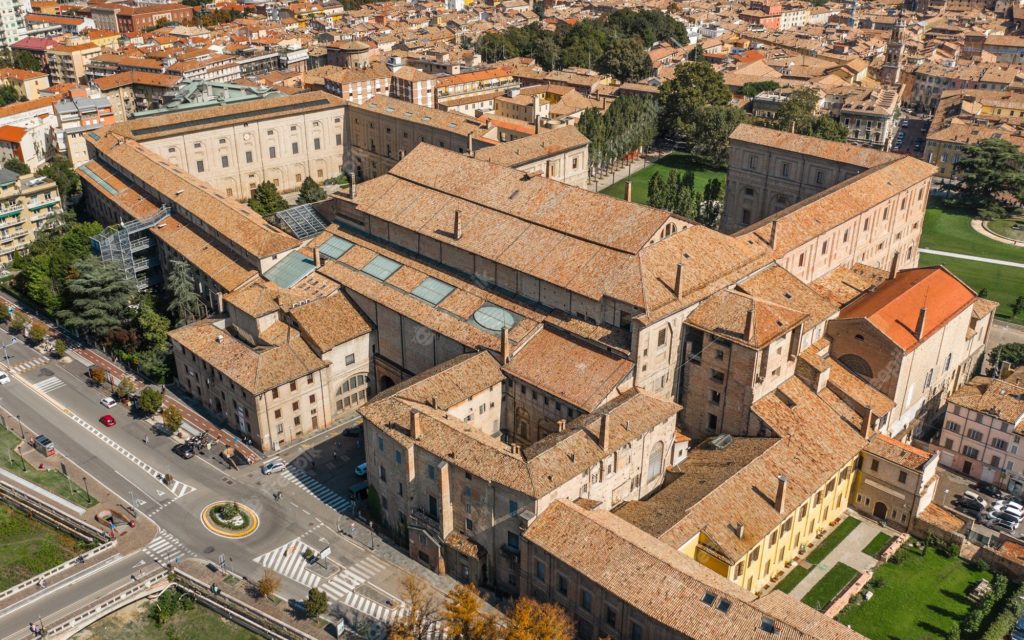

Another example is the Palazzo della Pilotta in Parma, which has been equipped with a monitoring system that includes predictive maintenance. This system uses sensors and AI algorithms to constantly monitor the structure and predict future maintenance problems. This has reduced maintenance costs by scheduling preventive interventions and ensuring long-term preservation of the palace itself.
To sum up, the overall benefits of intelligent monitoring of historic buildings and sites are:
In conclusion, the past offers many opportunities to preserve our future. Through monitoring and predictive maintenance, we can protect historical buildings for future generations and ensure our legacy is preserved forever.
Fill out the form at the end of the page to request information on products or partnerships.
Maybe not everyone knows that the Thames was declared biologically dead in 1957. Indeed, London’s famous river has worked as an open sewer for centuries, leading to many an epidemic of cholera until the government decided to do something about it in the mid-800’s - particularly after what is known as the Great Stink.
It wasn’t until the '60s that construction projects for the recovery of a bombed and destroyed London amended and improved the previous sewage system, sanitizing the waters and bringing the river back to life. In more recent days one could even enjoy the company of harbor seals up in Richmond Lock.
More recently, however, in 2018 the growing population of the British capital posed a new threat to the existing draining systems. The authorities found it hard to keep up with the daily management of gray water.
If we learned something from the Thames’s history, then we should know by now that the management of sewers and waters is of the utmost importance for the wellbeing of the cities population.
Monitoring and management of pieces of critical infrastructure such as sewers are usually carried out on a case-by-case basis or with sporadic, periodic maintenance activities. However, this has two main issues: they ignore whatever phenomenon happened in the interval between two maintenance operations and only repair whatever damage occurred beforehand, ignoring predictive maintenance for damages that might occur later.
Moreover, periodic mass interventions have a certain weight on the annual budget, both for the individual companies and the taxpayers - companies dealing with urban waters and sewers are usually public and funded by the government.
In the second place, urbanization and overuse of infrastructure become critical in this specific sector of civil infrastructure. Poor management of the sewage system can have disastrous effects on both the population’s health and the environment, leading to damages that can only be healed in years.
This means that companies are faced with no option but to allocate much of their budget on damage control activities rather than on improvement and best practices, slowing down the development and progress of technologies and methodologies to best manage the systems.
We can predict what happens in the future. Our platform centers around the chance to implement predictive maintenance civil infrastructure to avoid any potential problem before it occurs.
Through a distributed system of sensors specifically installed in strategic locations of the infrastructure, Sensoworks’s IoT platform gathers all the necessary, raw, yet incomprehensible data and translates them into intelligible, indexed information in specifically created dashboards. This allows both Sensoworks’s IoT platform and managers and supervisors to understand what was, is, and will be of the monitored piece of infrastructure and intervene timely if necessary.
In the case of sewer systems' tunnels and pipes, Sensoworks designed a solution based on sensors constituted by fiber optic cables up to 50 km long. For the monitoring of sewers, the sensors we employ exploit Brillouin light scattering along the optic fiber.
The change in the Brillouin frequency signals to the platform a change in the temperature and/or in the mechanic strain. Each cable is built to react to both the phenomena.
Sensoworks' projects work on “close loop” systems to reach better results in terms of spatial resolution. The difference between “close loops” and “open loops” depends on how light radiation is used: “transmitted” in the first case and “reflexed” in the second case.
Thanks to Sensoworks, sewers are constantly monitored (24h a day, 365 days a year) for more than 37 km of pipes. The platform is always looking for deformations, it constantly checks the water level, speed and flow rate and controls potential anomalies due to parasitic infiltrations.
This doesn’t only work for sewers. Sensoworks’s IoT platform is designed to be highly scalable and adaptable to several kinds of systems and infrastructures. Sensors following this strategy can be installed on gas and water pipes (for the former, Sensoworks employs a higher-frequency Distributed Acoustic System to better detect gas leaks) to monitor the heating system or water supply, for instance.
This way, managing authorities can carry out less, more precise interventions to contain both potential damages and maintenance costs - both operational costs and staff deployment. Moreover, the causes of damages for underground facilities can be difficult to understand and expensive interventions are needed to assess the reasons for faults and malfunctions. Sensoworks’s platform’s dashboard, instead, shows clear and indexed information with thresholds and limits you can set to notify you in case any value exceeds the safety limits. So you know in real-time what is happening and where.
Sensoworks’s mission is to provide solutions that support people in their everyday life. Infrastructure, today, is an integral part of it: our lives would be much more difficult without the infrastructural system of roads, bridges, tunnels, sewers, and so on.
Urbanization and the evolution of our lifestyles need to be matched by a constant improvement of the technology and the systems we use, even more so when confronted with an increasing number of people enjoying and exploiting civil infrastructure.
Sensoworsks believes in the potential of technology at the service of people. Sensing the future is the way we want to give value back to the community, predicting what’s next is how we want to empower everyone with a stronger infrastructure for all their needs.
Contact us to have more information on the topic and get your custom demo
According to a classification made by the University of Vienna, there are 6 factors that distinguish a smart city:
Each factor contributes to the achievement of a smart city where the gap between needs and satisfaction is filled. The technology that helps us make a city smart is the IoT (Internet of Things), where everything ideally "comes to life" thanks to appropriately installed sensors and a stable widespread wireless communication in every corner of the city. All data generated by sensors converge to a central ”brain”, where they are further elaborated through sophisticated AI algorithms, so that the "smart things" act accordingly to the humans’ preferences and habits.
The things become intelligent, break down spatial distance and allow you to satisfy all your needs in the shortest time possible, without having to even leave your house.
Although urbanization is not a strictly contemporary phenomenon, these last decades saw an exponential increase in the urban population. Only 15 years ago, the rural population was still the majority of people on Earth - only in 2007 the urban population exceeded rural areas for the first time in all history!
This should be enough to understand the massive change demography and urbanization went through. But most importantly, it should be enough to realize the huge impact this massive shift in our living habits had on the environment and on the society we are all part of. If we also add the simplification of travel and movement around cities, for tourism or work-related visits, and the ease of purchase for cars and other means of transport, then we can picture the increased complexity of society today.
If pollution, overpopulation, poor mobility were true three decades ago, today we find these to be exponentially amplified by a larger number of people living in urban areas as much as they are exacerbated by years and years of inefficient policies and inactivity. However, it is also true that today we have easier access to advanced technologies and solutions.
Today’s technologies help us to harvest and process the many data we need to assess critical situations or to increase maintenance and conservation efficiency. IoT is an incredible solution in this sense: it allows us to not only have a constant eye on the places sensors are installed on, but also to harvest all the necessary data and to send them to a processing terminal and to translate them into understandable information.
Data transmission technologies have developed a lot in recent years and allow for a high level of connectivity in every corner of the city: just think of how we have evolved from 2G to 5G technologies in just under 30 years, with new 6G technologies currently under development. This technological evolution encouraged and allowed us to send and receive quantities of data unthinkable just until a few decades ago. Not only, at the same time new data recording and security techniques are available too, such as blockchain technology, which encrypts the data in unchangeable ledgers of data for future reference and use.
All of this led to wider involvement of technology and companies in the public life, bringing the private sector and the suppliers of new solutions closer to the public administrations. Today, it is more common to see contracts and partnerships between the public and the private sectors for the monitoring and supply of technologies for infrastructure and construction sites. This gives birth to a whole new way of conceiving the expansion and control of cities’ infrastructure and utilities.
Cities all around the world are already trying to take advantage of these new technologies with an array of new solutions, methodologies and devices such as sensors, controllers, communication devices, cameras, and so on. However, installing such devices is only the first step in the transformation to a smart city. The fundamental step is the implementation of a “brain”, a central terminal that allows the dialogue between devices and people.
An example of a solution by means of data monitoring is that of mobility and traffic congestion. Gathering and translating the necessary data can help us monitor traffic and parking circulation or support greater amounts of traveling vehicles without having to incur in the costs of widening urban roads or adding new roadways and parking lots.
Solutions that entail the use of sensors embedded into the floor to register whether a vehicle is parked in the space right above them or placed on the entrance and exit of a car park might give us an idea of how many parking spaces are available. While a combination of sensors such as license plate readers, in-vehicle sensors, CCTV cameras to check congestion, in-road embedded sensors to monitor the passage and the staying of cars, it gives us a good assessment of the ongoing traffic situation.
Although this is usually confined to only a specific, critical area, rather than the city on its whole, new V2I methodologies (“vehicle to infrastructure” as opposed to V2V, “vehicle to vehicle”), instead, can give a more holistic view of the city’s road system. For instance, V2I corridors installed on the road of smart cities can alert the driver of upcoming traffic or even weather conditions beforehand, suggesting that they might want to slow down or follow an alternative route so as not to get stuck in traffic later on the way.
However, although the new trends on micromobility and a larger adoption of alternative means of transportation, a poor infrastructural use of roads is still a major problem afflicting big cities and capitals around the world. Traffic jams take a heavy toll on our environment, besides posing a problem to noise pollution and having all of us commuters lose time stuck on the road or in front of outdated traffic lights. As much as it may sound weird: yes, the traffic light system we currently use in much of the world is proven to be outdated.
Moreover, parking and traffic are not only a major cause of jams and frustration, but it also affects an important source of revenue for the municipality. Parking, indeed, is usually the second or third largest source of income for towns and cities. A poor use of parking spaces or of infrastructure - such as the lack of multi floor parking compounds in city centers - can have terrible repercussions not only on the environment, but also on the city finance.
Advanced Traffic Management Systems (ATMS) and Advanced Traveler Information Systems (ATIS), however, mainly rely on fixed point, eulerian measurements from loop and radar detectors. These can collect data relating to flow, speed and occupancy (as in the examples we’ve seen earlier) but cannot provide trajectory-based information such as direct trip observations or the time of travel on routes - that is lagrangian measurements. This means that we are missing important clues on the behavior of traffic to better understand how to improve our cities.
The data harvested from different systems employing lagrangian measurements, together with already existing tech solutions and measurements, would allow us to to have a more holistic view of how the city works and to further instruct drivers and passersby on the ongoing situation of traffic congestions and parking not only on given areas at a certain time, but also predicting the flow of cars, travel time, departure time of cars from parking spaces and so on.
Although we already saw many innovations taking place in cities such as Shanghai, Pittsburgh, London, New York, Milan, and so on, the space for innovation and for further progress is wide open and we should not stop researching further to simplify and improve our cities and lives.
Urban contexts are various and different, each with their needs and peculiarities. That is why Sensoworks developed a highly customizable platform that can be employed across different industries.
All our products are designed by specialized engineers. This is to ensure max efficiency when it comes to our features, architecture and UX to both private and public customers. Moreover, we work in close collaboration with HW manufacturers and integrators. The ecosystem we built - and are constantly improving - allows us to design our platform to be a real end-to-end solution, from the sensors our hardware partners produced to the integration of our services to the customer’s entire architecture.
Whether our customers are private companies or public institutions, we developed our platform to be as flexible as it gets to allow you to start up with low costs, to grow quickly and to integrate with new, future tools (and cut off outdated software).
We pay close attention to the use of data, which have to be constantly available and immediately turned into information. We do this thanks to our Edge component, which allows data to be analyzed in real time by peripheral devices. In case an event occurs, the platform takes the necessary decisions on the very same place, allowing for immediate answers with low latency.
The Edge computing component, moreover, allows for the recovery of data from different kinds of devices connected to the same edge gateway, which works as a hub for the whole connectivity system. This way, data is sent to the Cloud platform from one only gateway. The union of more devices together avoids individual one-to-one communication (sensor/terminal) and cuts down energy consumption, improving the overall performance of connectivity in smart cities.
Speaking of smart cities, our work is not aimed only at managing parking problems. We have a wider goal: to create a unique infrastructure to gather all the data related to the city’s life and activities and to integrate it with third-party software and applications as well, supporting the entire community.If you want to know more about how our platform works and discover the whole range of monitoring solutions we provide, write to us. Write a comment or come visit us on sensoworks.com.